Introduction
Many educational institutions interchangeably use "staff" and "faculty." This is a widespread misunderstanding about word suit use among individuals. The primary distinction between staff and faculty is that staff refers to an organization's personnel, whereas faculty refers to academic staff members such as instructors, lecturers, or professors. The term "faculty" refers to the institution's academic personnel, including your subject professors and other teachers at your school or college. On the other hand, staff refers to the organization's administrative personnel, such as accountants, office assistants, counselors, registrars, secretaries, and others.
This article includes a table outlining the distinctions between faculty and staff and a podcast highlighting their use.
Faculty vs. Staff
Faculty members, frequently recognized experts in their fields, are primarily concerned with imparting knowledge to students and conducting groundbreaking research. On the other hand, staff members are in charge of performing the essential administrative and support functions that keep the organization running smoothly and effectively. Staff members work tirelessly behind the scenes to ensure the success of the faculty and students, whether they are managing finances, providing IT support, or maintaining facilities.
While these two groups' responsibilities may overlap in some ways, their distinct contributions allow a well-rounded and thriving organization to exist.
The teaching staff of an educational institution is referred to as faculty. In contrast, the non-teaching personnel, referred to as staff faculty, is a collection of professors who provide instruction to pupils in a school or college setting. In general, the phrase "staff" refers to the entire group of people who work for the company. The instructors at a school or institution are referred to as faculty, in contrast to staff, which refers to any organization's personnel. The faculty's working hours are erratic, although the staffs are consistent. The faculty is in charge of carrying out the organization's instructional tasks. Staff personnel, on the other hand, undertake administratively and support responsibilities. The faculty's primary responsibility is to teach information to students, whereas the staff's primary responsibility is to provide administrative support. Faculty salaries are determined by their rank in the educational institution, whereas staff salaries are determined by their position. Faculty members must complete their studies by the institution's norms and criteria. On the other hand, a staff member's educational qualification is determined by their designation, with the more significant the designation, the higher the salary.
Their rank determines a faculty member's compensation in the educational institution. In contrast, a staff member's income is determined by their position/level in the organization, with higher levels attracting more outstanding salaries. Faculty requirements are based on the institution's norms and criteria, while employees are hired based on their educational qualifications. Staff personnel includes secretaries, assistants, deans, presidents, registrars, and clerks, while faculty members include associate professors, assistant professors, substitute professors, lecturers, researchers, and teachers. Faculty members work flexibly, whereas staff members work on a set schedule. Staff workers work on a defined schedule, whereas faculty members operate on a flexible schedule.
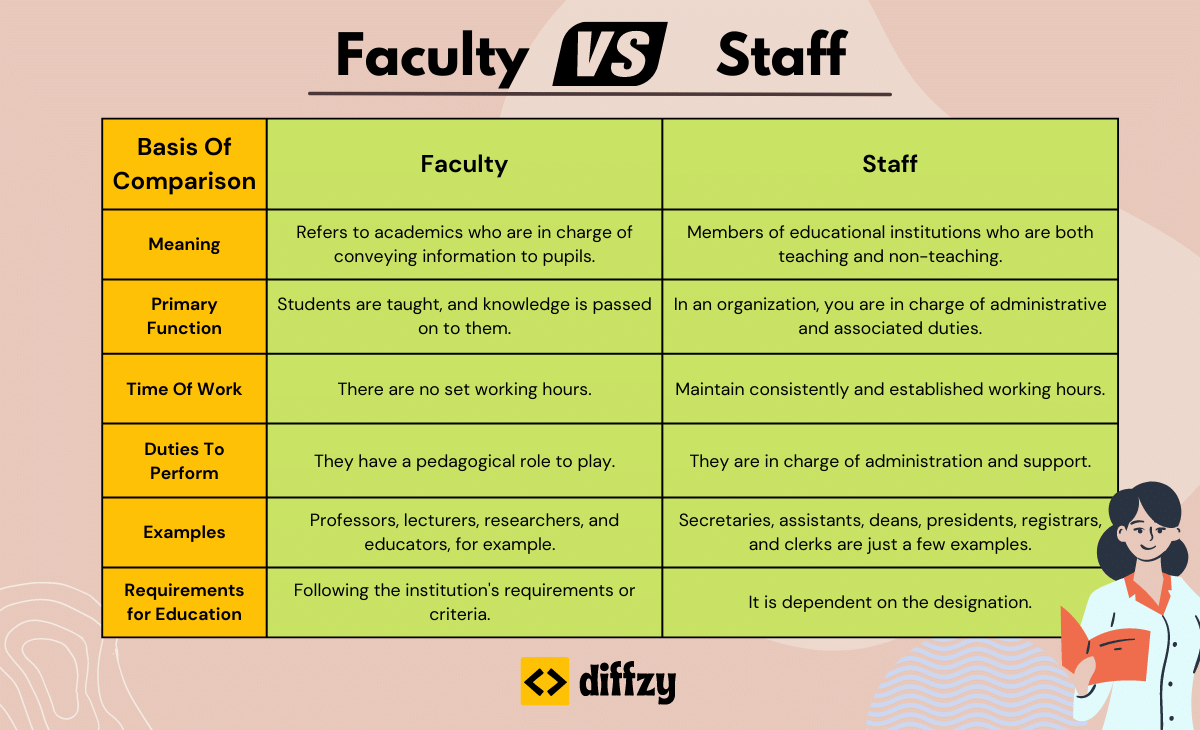
| Basis of Comparison | Faculty | Staff |
| Meaning | Refers to educators who are in charge of conveying information to students. | Members of educational institutions who may be involved in teaching or non-teaching roles. |
| Primary Function | To teach students and impart knowledge to them. | To handle administrative and associated duties within an organization. |
| Work Hours | No set working hours. | Consistent and established working hours. |
| Duties | They have a pedagogical role to play. | They are responsible for administrative and support tasks. |
| Examples | Professors, lecturers, researchers, and educators. | Secretaries, assistants, deans, presidents, registrars, and clerks. |
| Educational Requirements | Depends on the institution's requirements or criteria. | Depends on the specific job designation. |
What Is a Faculty?
Faculty refers to a group of educators, such as professors or teachers, whose goal is to impart information to students at a school, college, or university. So expressed, faculty refers to the members of an educational system's teaching or academic staff employed to educate pupils. The teaching staff of a school, university, or other private educational institution is faculty. They are in charge of passing on information to students.
Professors, instructors, lecturers, researchers, and teachers are all examples of faculty. These are passionate about teaching students who also specialize in various fields of study and typically teach various courses based on their areas of expertise. On the other hand, faculty in universities and colleges refer to divisions based on a topic area or a group of related subjects. Faculty of law, engineering, medicine, business, and the arts are just a few examples of universities' faculties.
A faculty consists of instructors, lecturers, researchers, scholars, and professors of various academic positions, such as associate professors, assistant professors, etc. They are experts in various topics and teach a variety of subjects at the university.
Different Types of Faculty
We Have Different Types of Faculty, Which Are Listed Below:
Instructor
An instructor usually possesses a Master's degree or similar, has completed almost all of the prerequisites for a doctorate or equivalent and is believed to be primarily successful as a teacher. The instructor is the entry-level position for people who have recently finished post-doctoral, residency, or fellowship training. In addition, this position is for new professors who have earned an M.D., Ph.D., or similar degree and have the potential to progress academically.
Assistant Professor
In general, an assistant professor possesses a Ph.D. or professional degree or equivalent, demonstrates a dedication to teaching and high-quality academic or professional activity, and engages in University activities at least at the department level.
Associate Professor
An associate professor generally meets the requirements for appointment as an assistant professor, has a national reputation as a scholar or professional, demonstrates a high level of teaching proficiency and commitment, and demonstrates public, professional, or University service outside the department.
A professor generally satisfies the standards for appointment as an associate professor and has an outstanding record of success that leads to an international or, as appropriate, national reputation in their specialty.
Clinical
Appointments focus on practical education and the application of practical expertise. The term refers to faculty members whose significant activity is clinical or public health practice and related teaching. The letter of appointment specifies the duties, periods of appointment, and salary (if any) of such individuals.
Such roles are designated by several titles, including:
- Clinical Assistant
- Professor Clinical
- Associate Professor
- Clinical Professor
- Clinical Instructor
Lecturer
A lecturer is a faculty member assigned primarily to deliver teaching for a set period, either full-time or part-time, as mentioned in the appointment letter. The fundamental credentials and standards expected of a lecturer differ depending on the University's Schools and Colleges. Still, the title shows excellent teaching skills and a relevant foundation of scholarly work or professional competence and success.
What Is a Staff?
The term "staff" has a broad definition since it is a collective phrase that refers to all personnel working in an organization who execute routine activities of the institution, such as executive, operational, administrative, logistical, sales, support, and maintenance.
When we talk about educational institutions, we're talking about people with a wide range of educational backgrounds. They can also be classified into academic staff and general personnel. The academic staff is in charge of educating students. An organization's personnel are classified as staff based on their functional divisions. They are usually in charge of the organization's internal operations. Administrative personnel, accounting personnel, counseling personnel, and marketing personnel are just a few examples of staff.
The primary job of the employees in the organization is to conduct administrative and associated responsibilities. Therefore, they can also refer to university employees. However, university staff is divided into academic staff and general employees. Whereas general staff refers to employees, academic staff refers to faculty.
Employees of various ranks are included in the staff
- Top Level Staff- Administrators, deans, directors, and presidents are examples of top-level personnel.
- Middle-Level Staff- Employees at the middle-level conduct in-office and support activities such as counselors, cashiers, assistants, etc. They are also in charge of admissions, security, paperwork, and papers.
- Low-Level Staff- security guards, servants, gardeners, cleaners, and other low-level employees are examples of low-level employees.
Different Types of Staff
We have different types of staff, which are listed below :
Full-Time Employees
Employees who work full-time work an average of 40 hours per week and are entitled to benefits such as health, dental, vacation days and paid time off are considered full-time. The employer often provides an employment agreement that describes the employee's obligations, the scope of their services (hours and days of work), benefits, termination, notifications, and applicable law.
Teachers, editors, etc., are some examples of full-time employees.
Part-Time Employees
Part-time employees are those who work fewer than 40 hours per week and are usually paid by the hour rather than by the hourly wage." Although they may not be entitled to benefits, these workers are still considered corporate employees. Students, mothers and fathers, retirees, and other jobs are examples of part-time employees.
Temporary Employees
Temporary employees are recruited for a specific length of time, such as six months. They may also be engaged for a specific project and then terminate their employment with the organization after the project is over. Fixed-term, project- or task-based contracts and seasonal or casual work, including day labor, are all included.
Seasonal Employees
Seasonal workers are recruited for a specific period to meet a company's demands. They often assist with increasing job demand or seasonal employment during certain seasons of the year. For example, the most prevalent type of seasonal work is in the agricultural industry.
Main Differences Between Faculty and Staff in Points
The essential distinctions between faculty and staff are outlined below:
- The faculty is defined as a collection of professors who teach pupils in school or college. In general, the phrase "staff" refers to the entire organization's employee group.
- The term "faculty" refers to a school or college's educators, in contrast to staff, which refers to any organization's personnel.
- A faculty member's role is to educate pupils on the assigned standard or class. In contrast, a staff member's job fulfills all administration and support responsibilities.
- The term faculty refers to instructors or professors at schools or colleges, whereas the phrase staff refers to all other personnel in an institution other than teachers.
- Professors of various grades, such as associate professors, assistant professors, substitute professors, lecturers, researchers, instructors, and so on, maybe members of the faculty. In contrast to staff, which comprises secretaries, assistants, deans, presidents, registrars, clerks, etc.
- The institution's norms and criteria determine the education requirements of faculty members. A staff member's educational qualification, on the other hand, is determined by their designation; the more significant the designation, the higher the salary.
- Their rank determines a faculty member's compensation in the educational institution. In contrast, a staff member's income is determined by their position/level in the organization, with a greater level attracting a higher salary.
- Faculty work on an irregular schedule, whereas employees work on a set schedule.
- Faculty are institutes employed for various tasks, while the staff is workers engaged for specific positions.
Similarities Between Faculty and Staff
Faculty and staff are similar in that they-
- both represent members of an organisation.
- Both members have a set of academic credentials.
- Both members contribute to the operation and management of an organisation.
Conclusion
As a result of the preceding explanation, it is pretty evident that there is a significant difference between these two words. The staff has a considerably broader reach than the faculty because the latter is incorporated into the former. Furthermore, the word faculty is limited to education, whereas workers in any organization are referred to as staff. Faculty and staff are connected with educational institutions such as schools, colleges, and universities. People participating in these institutions might be from academic or non-academic backgrounds. The primary distinction between faculty and staff is that faculty refers to a group of professors who educate students, whereas staff refers to those who conduct labor other than teaching. Accountants, assistants, counselors, secretaries, office assistants, security crew, clerks, registrars, deans, and other positions are assigned to staff members based on their educational backgrounds. Staff working hours are more consistent than academic working hours. Faculty members are appointed based on their educational credentials and assigned responsibilities, such as which class they may teach, which subjects they can teach, and so on. Staff refers to all institution employees other than a college or a school. The term "faculty" can only be applied to educators in a teaching institution.
References
- “Faculty.” FACULTY | Meaning, Definition in Cambridge English Dictionary, 7 Sept. 2022, dictionary.cambridge.org/dictionary/english/faculty.
- “Academic Personnel - Wikipedia.” Academic Personnel - Wikipedia, en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Academic_personnel. Accessed 15 Sept. 2022.
- “Faculty (Division) - Wikipedia.” Faculty (Division) - Wikipedia, 1 Sept. 2018, en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Faculty_(division).
- “What Do Faculty Do? | AAUP.” AAUP, 28 July 2006, www.aaup.org/issues/faculty-work-workload/what-do-faculty-do.
- “Staff.” STAFF | Meaning, Definition in Cambridge English Dictionary, 14 Sept. 2022, dictionary.cambridge.org/dictionary/english/staff.
- “Faculty.” FACULTY | Meaning, Definition in Cambridge English Dictionary, 14 Sept. 2022, dictionary.cambridge.org/dictionary/english/faculty.