Introduction
Communication is the most effective way of interaction between human beings. A confident, precise, and clearer conversation makes a huge impact on every kind of relationship. Effective communication skills can help you achieve high goals in almost every area of your life. Whether it is personal or professional. Having an innovative idea is not enough. Conveying it to the audience and making them understand it is important too.
Enhancing communication skills is crucial nowadays. In this article, we shall have a look at two types of communication that are purposive communication and oral communication.
Oral Communication vs. Purposive Communication
The key distinction between oral and purposive communication is that the Oral communicates with a purposeful vocabulary. Purposive communication is an undeveloped style of communication that is formatted to efficiently and effectively transmit concepts and ideas in cultural and metaphysical spheres. Oral communication, on the other hand, is beneficial when it comes to problem-solving. Direct input, recommendations, or inquiries from the receiver are possible. Decisions should be made automatically due to immediate reactions on the other end.
Purposive communication terms are based on writing, speaking, and conversing to and with varied crowds, whereas oral communication is focused on purposeful language. Oral communication allows for holes and fills to lighten the discussion, whereas purposeful communication allows for complete communication.
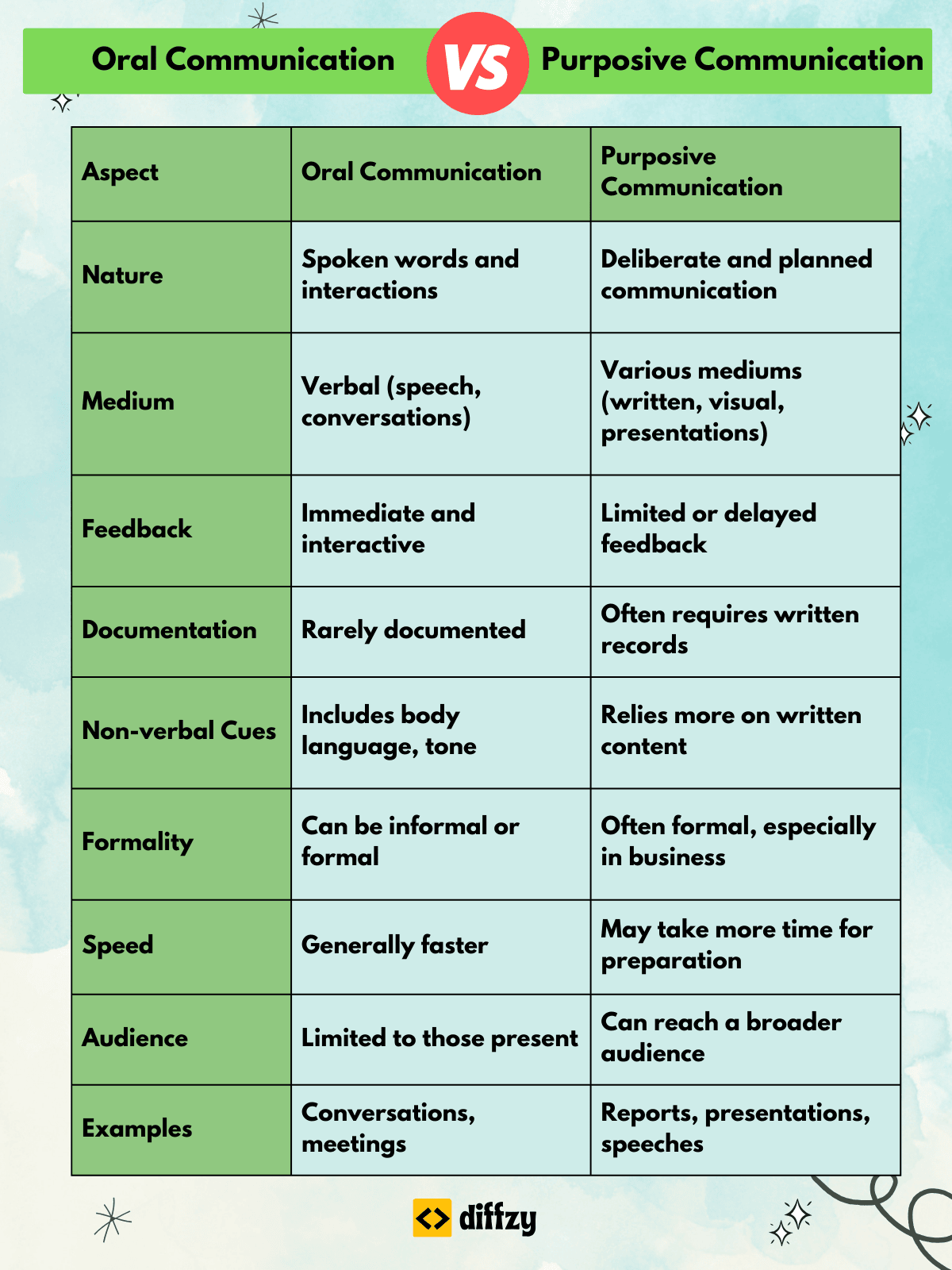
Difference between Oral Communication and Purposive Communication in Tabular Form
| Parameter | Oral Communication | Purposive Communication |
| Mode of the Conversation | Only speaking | Speaking, writing, or talking |
| Spontaneity. | Oral communication is often spontaneous and can be improvised | Purposive communication is pre-planned, well-structured, and not spontaneous. |
| Feedback frequency | Prompt feedback can be obtained. | Less frequent feedback is obtained as compared to oral communication. |
| Record | No proof of the conversation is there. | Record of purposive communication is maintained. |
| message conveying speed | prompt | Slow |
| literacy | since only words are supposed to be spoken no literacy is required to have this type of conversation | Literacy is important. |
| Possibility of misunderstanding | High | very low |
What is Oral Communication?
In simple words, oral communication refers to communication through the use of spoken words. It's a type of verbal communication in which you express yourself, present ideas, and share information. Anything which is spoken with someone is oral communication.
Examples of oral communication could be, speeches, conversations with friends or family, presentations, meeting conversations, and so on.
The conversation could be direct or over video conferencing or telephonic. Oral communication leads to the formation of reliability and trust. Oral communication is more effective than sending a text message or sending an email. To avoid misconceptions and confusion during crucial and sensitive interactions, oral communications are worth it to get your point across.
Importance of Oral communication
- Oral communication lets you communicate and convey the message faster and it allows you to get a real-time reply.
- It saves a significant amount of time as compared to written communication.
- Because oral communication is direct, there is a high level of understanding and transparency.
- We get a prompt reply that is the feedback that lets us make decisions faster. Hence delay in taking decisions is avoided.
- Saves a significant amount of time, money, and effort.
- When it comes to problem-solving, oral communication is the most effective. Conflicts, disputes, and a variety of other issues/differences can all be resolved by talking about them.
- To create a bond with someone at the workplace or in personal life, oral communication is the most effective medium.
- At the organizational level, oral communication is necessary since exchanging innovative ideas is most important for growth and that is not possible without oral conversation.
Limitations
- At the business level, a formal and organized way of communication is required. In such cases, oral communication cannot be used.
- Because oral communication is more informal and less ordered than written communication, it is less credible.
- Oral communications could be unproductive at times and could consume unnecessary time.
- Written communication is preferred over oral, in the case of businesses. Oral communications are unsteady.
- Because the information is incomplete and may be missing basics, there may be misconceptions.
- Except in investigation work, the spoken conversation is rarely utilized as a legal record.
Examples of Oral Communication
- Team meetings, business meetings, and other face-to-face meetings are all examples of face-to-face meetings.
- Telephone calls
- Speeches, lectures, and conferences are examples of public presentations.
- Interviews via teleconferences or videoconferences.
Types of Oral Communication
You can more successfully communicate ideas or express emotions when you employ multiple ways of communicating. You convey your thoughts aloud to another individual in verbal communication. The tone of your voice is another piece of information you might transmit during a conversation. The four modes of verbal communication are listed below:
Interpersonal Oral Communication
Interpersonal communication is the process of two or more individuals exchanging information, ideas, and feelings. Face-to-face interaction employing speech, facial responses, nonverbal cues, and gestures is common. The efficiency with which one communicates with others is used to evaluate one's interpersonal communication skills.
Internal employee communication, customer meetings, employee performance reviews, and project discussions are all instances of interpersonal communication used in businesses. Furthermore, online chat rooms now account for a major portion of workplace interpersonal interactions.
Intrapersonal Communication
Intrapersonal communication is the process through which a person communicates with himself or herself, functioning as both a sender and recipient of messages, and comprises the use of unsaid words to engage in conscious self-talk and inner speech.
Intrapersonal communication can thus be characterized as communication with oneself, which includes self-talk, acts of imagination and imagery, as well as recall and recollection. You see on your phone screen that your friends are headed to your favorite restaurant for dinner.
Intrapersonal oral communication includes things like talking to yourself, reading aloud, writing, thinking, meditating, singing, and analyzing.
Group discussions
When there are more than two people present, small group conversations may occur. The number of participants may be modest enough that each individual can interact and communicate with others. The majority of small group communications are focused on performing specific tasks or achieving specified objectives. Small group communication can take many forms, including board meetings, weekly team meetings, and press conferences. Small group communication in the workplace can enable people to fill informal roles, collaborate, and establish a sense of belonging.
Social / public communication
Strategic communication to deliver ideas, programs, though, presentations, data, propaganda, etc., to the masses, the public, students, or niche audiences is known as public communication. In every country, public communication plays a critical role in disseminating ideas and information to the public.
Oral public communication includes events such as public speaking, conferences, seminars, and press conferences.
How to enhance Oral Communication?
Everyone must be able to effectively communicate vocally. They are quite useful in both personal and professional contexts. Here are a few tips to improve oral communication effectively.
- Thinking before talking is important. Talk slowly and thoughtfully. This will help eliminate unnecessary and awkward pauses in between due to a lack of words or thought. Before you begin to talk, take a moment to clarify your thoughts in your head.
- Use understandable language and small sentences. Avoid using complex vocabulary and make the speech as clear as you can.
- Have a good knowledge of the topic you are going to talk about. An adequate knowledge will bring confidence while speaking. Body language, direct eye contact, confident language, and command of words will help to build the confidence that is needed. This improves the credibility of the speaker.
- Change the tone of the speech from time to time according to the matter of the speech and emotions. Avoid speaking in a monotonous tone. This will increase audience engagement.
- Lastly, be a good listener. Every speaker has to be a good listener first to be able to understand the audience’s perspective. It shows the individuals you're conversing with that you genuinely care about their ideas, as well as that you understand their needs.
What is Purposive Communication?
Purposive communication is defined as the use of language in writing, speaking, and presenting for a variety of audiences and goals. Purposive communication is done with a specific goal in mind; it is not spontaneous since it is not done on the spur of the moment, winging it, or blurting out whatever comes to mind.
Importance of Purposive Communication
- Purposive communication is critical in human life, especially when it comes to connecting with others and forming relationships.
- Purposive communications also necessitate the appropriate format, medium, and language in order to effectively communicate the message and improve team performance.
- Purposive communication is utilized to achieve a certain goal as well as to preserve professionalism.
Types of Purposive Communication
Verbal
Recorded group discussions, conference calls, official meetings, speeches, interview sessions, and so on are examples of purposive verbal communication. In this, the communication is planned and well-structured. These conversations don’t take place spontaneously.
Non-verbal
Non-verbal purposive communication can be defined as reacting in the most effective way without using words. For example, appreciative smiling at an idea stated by the speaker or nodding to portray comprehension of the context spoken by the speaker.
Giving an accurate reply or reaction is as important as giving a speech.
Written
The act of writing, typing, or printing to communicate information is referred to as written communication. It's beneficial since it keeps track of information for future use. Books, pamphlets, blogs, letters, memoranda, and other forms of writing are frequent ways to disseminate knowledge. In the office, textual communication takes the shape of emails and chats.
Visual
Using images, art, drawings, sketches, charts, and graphs to communicate information is known as visual communication. During presentations, visuals are frequently utilized to supplement written and/or vocal content by providing valuable context. Because everyone learns in a different way, visual communication may be more effective for some people in absorbing ideas and information.
Examples of Purposive Communication
Listening, grasping, criticizing, and responding to live or recorded discussions, speaking publically with confidence, explaining genuine texts or text in your own words with various illustrations, writing technical reports and academic studies, and preparing a presentation are a few instances of purposive communication.
Main Differences Between Oral Communication and Purposive Communication in Points
- Conversation with the use of words spoken is known as Oral communication. Purposive communication could be oral, spoken, or written.
- Planning is done before conducting purposive communication. It is well structured and not spontaneous. All the members involved are aware of the subject matter. On the other hand, oral communication is spontaneous. Impromptu topics can be added and discussed in this type of conversation.
- No record is maintained in oral communication hence there is no proof to present in the future of having the conversation happen. In purposive communication, every record of the conversation is maintained as proof in the future.
- Oral communication can be done even if a person is illiterate. There is no need for written literacy to have oral communication. Purposive communication needs writing skills, speaking skills, command of the language, and hence literacy.
- Since oral communication is spontaneous there are higher chances of getting misunderstood. On the contrary, purposive communication is absolutely planned and structured. Chances of misunderstanding are lessened to the great extent.
- Making understanding the concept to the audience easier in oral communication. Any issue faced by the listener can be solved promptly and effectively. The speed of understanding is comparatively lesser in the case of purposive communication.
- A speaker may get feedback immediately in oral conversations but in purposive conversations, delay in getting feedback can be experienced.
- Purposive communication terms are based on writing, speaking, and conversing to and with varied crowds, whereas oral communication is focused on purposeful language.
Conclusion
Communication is very important as it is a basic activity an individual does in a day. The conversation is needed to express feelings verbally or deliberately. Oral and purposeful communication can be formal or informal, depending on the situation. Purposeful and oral communication can be found in many different forms. Formal conversations include formal discourses, business addresses, seminars, and TED talks. However, when dealing with a famous person, we speak in a less formal manner. Although there is a distinction to be made between oral and purposeful communication, both skills are essential. Each of these forms can be found in almost any situation.

